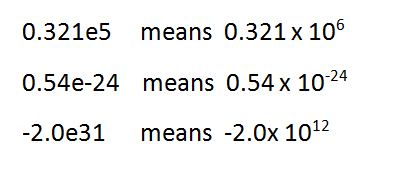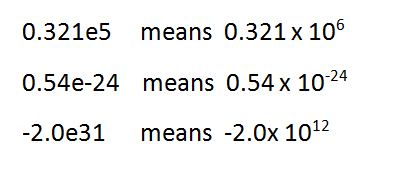Fundamentals of C Programming
Identifier:
An identifier is a name having a few letters, numbers and a special type of character. It is used to identify a variable, function, or symbolic constant. An identifier can be written with a maximum of 31 characters.
Example:

Tokens:
C program has punctuation marks, keywords and operators as the smallest individual units are referred to as Tokens.

Keywords in C:

Note: All the keywords must be written in lowercase.
Constants :
Any unchanged value in a program during the program execution is called constant. There are mainly two types of Constants in C language.
1. Numeric Constants
2. String or Character Constant
Numeric Constants :
There are two types of numeric constants.
(i) Integer Constant: An integer constant is a signed or unsigned whole number.
Example: -25, +25
(ii) Real or floating-point constant: Any signed or unsigned number with a fractional part is called real or floating-point constant. A real constant can be written in decimal or exponential form.
Example:
- Decimal form
0.542
+355.0
-3.14 - exponential form